Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 8 is an important year in a student’s life and Maharashtra State Board Science is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 8 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Book syllabus.

Question 1: Use Whittaker method to classify bacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae, prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes.
Answer: According to Robert Harding Whittaker, given below are the characteristic features of bacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae, prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes:
1. Kingdom Monera
2. Kingdom Protista
3. Kingdom Fungi
4. Kingdom Plantae
5. Kingdom Animalia
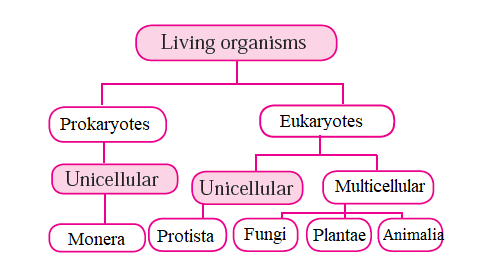
Question 2: Complete the five kingdom method of classification using living organism prokaryotes, eukaryotes, multicellular, unicellular, protista, animals, plants, fungi.
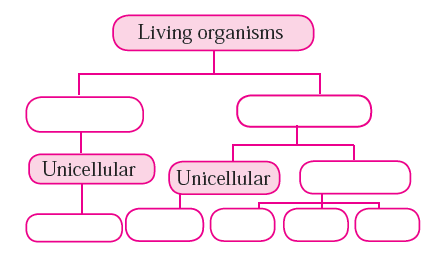
Answer:
Question 3: Find out my partner
| A | B |
| Fungi | Chlorella |
| Protozoa | Bacteriophage |
| Virus | Candida |
| Algae | Amoeba |
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Fungi | Candida |
| Protozoa | Amoeba |
| Virus | Bacteriophage |
| Algae | Chlorella |
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic |
Question 4: State whether the following statements are true or false. Explain your statement.
a. Lactobacilli are harmful bacteria.
b. Cell wall of fungi is made up of chitin.
c. Organ of locomotion in amoeba is pseudopodia.
d. Tomato wilt is a viral disease.
Answer: a. Lactobacilli are harmful bacteria.- False
Lactobacilli are not harmful bacteria. They are mostly found in the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals. They are an important component of dairy products such as milk, yogurt, ghee, etc.
b. Cell wall of fungi is made up of chitin.- True
c. Organ of locomotion in amoeba is pseudopodia.- True
d. Tomato wilt is viral disease.- True
Question 5: Give answers:
a. State the merits of Whittaker’s method of classification.
b. Write the characteristics of viruses.
c. Explain the nutrition in fungi.
d. Which living organisms are included in the kingdom Monera?
Answer: a. Whitakker ’s method of classification has the following merits:
b. The various characteristics of viruses are:
c. Fungi are called saprophytes because of their mode of nutrition. It is a nutrition mode in which an organism obtains its nutrients from dead or decomposed organic matter.
d. Organisms with the following characteristics are included under the kingdom Monera:
Question 6: Who am I?
a. I don ’t have a true nucleus, cell organelles or plasma membrane.
b. I have nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles.
c. I live on decaying organic matter.
d. I reproduce mainly by cell division.
e. I can produce my replica.
f. I am green, but don ’t have organs.
Answer:
a. I don ’t have a true nucleus, cell organelles or plasma membrane. –Monera
b. I have nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles. –Protozoa
c. I live on decaying organic matter. –Fungi
d. I reproduce mainly by cell division.- Bacteria
e. I can produce my replica. –Viruses
f. I am green, but don ’t have organs. –Algae
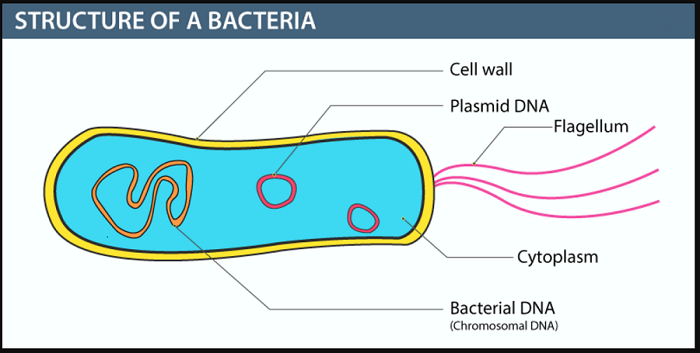
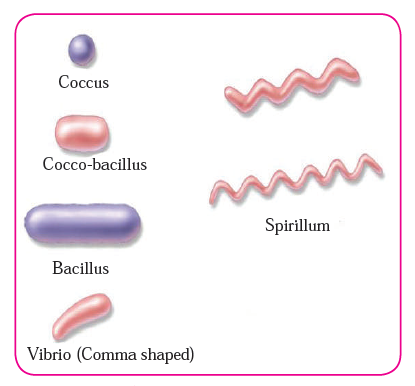
Question 7: Draw neat and labelled diagrams.
a. Different types of bacteria
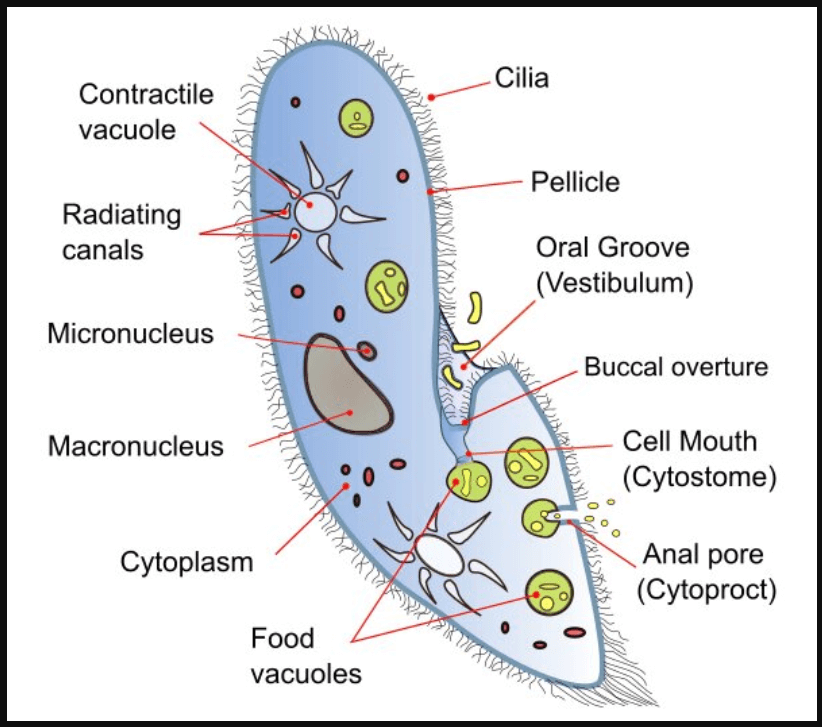
b. Paramoecium
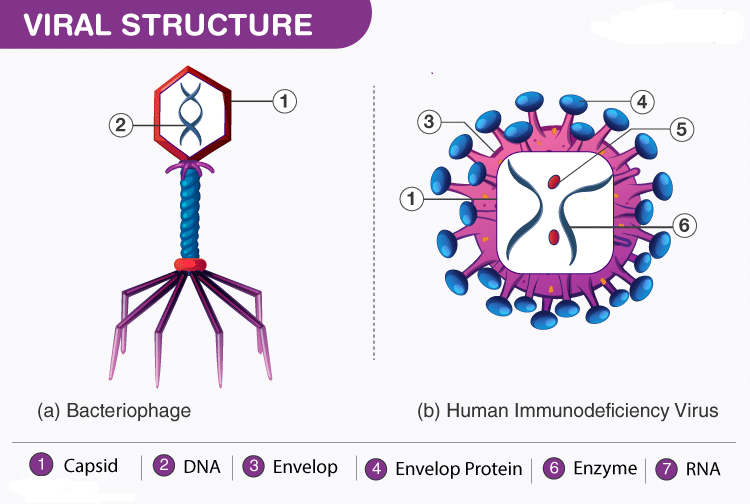
c. Bacteriophage
Answer: Given below are the labelled diagrams:
a. Structure of bacteria and its different types
b.Paramoecium
c. Bacteriophage
Question 8: Arrange the following in ascending order of size Bacteria, Fungi, Viruses, Algae.
Answer: Viruses →Bacteria →Fungi→Algae
Question 1: What is Biological classification?
Answer: Biological classification is the process of dividing living organisms into groups and subgroups.
Question 2: How many species of living organisms are found on the earth?
Answer: There are around 87 million species of living organisms that are found on the earth which includes both land and sea.
Question 3: What are the different groups of classification of living organisms according to Whittaker?
Answer: Robert Harding Whittaker (1920-1980), an American Ecologist divided living organisms into 5 groups in 1969. These include:
1. Complexity of cell structure
2. Complexity of organisms
3. Mode of nutrition
4. Life style
5. Phylogenetic relationship
Question 4: Name the different categories of living world mentioned by Carl Linnaeus.
Answer: In 1735, Carl Linnaeus divided the living world in two kingdoms –
1. Vegetabilia
2. Animalia
Question 5: Mention the categories of kingdoms by Haeckel.
Answer: In 1866, Haeckel considered three kingdoms of living organisms –
1. Protista
2. Plants
3. Animals
Question 6: What are the different categories of living organisms created by Chatton?
Answer: In 1925 –Chatton created two groups of living organisms namely,
1. Prokaryotes
2. Eukaryotes
Question 7: What are the four kingdoms of living organisms mentioned by Kopland?
Answer: In 1938 Kopland divided living organisms into four kingdoms –
1. Monera
2. Protista
3. Plants
4. Animals
Question 8: In kingdom Monera, what are the different types of bacteria?
Answer: Different types of bacteria and blue green algae are found in the kingdom Monera. Tiny movable rod-like microbes called lactobacilli bacteria are found in this kingdom. These can be observed under a high power of compound microscope.
Question 9: Define Protista.
Answer: Protista are unicellular organisms with a well defined nucleus which are covered in a nuclear membrane. They have pseudopodia or hair-like cilia or whip-like flagella meant for locomotion.
Question 10: Explain the shape of living organisms in the Protista kingdom.
Answer: Living organisms in the Protista kingdom are motile microbes which have an irregular shape, which can be observed under a low power and high power microscope.
Question 11: Give examples of Autotrophs and Heterotrophs in the Protista kingdom.
Answer: Examples of Autotrophs are Euglena, Volvox that contain chloroplast.
Examples of Heterotrophs include Amoeba, Paramoecium, etc.
Question 12: Define Fungi.
Answer: Fungi are non-green, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms. They feed mostly upon dead organic matter. Examples- Baker’s yeast, Aspergillus (Fungus on corn), Penicillium, Mushrooms.
Question 13: What is Bacteria? How is it formed?
Answer: Bacteria are unicellular, independent or parasitic organisms. They usually reproduce by simple binary fission. They grow vigorously under favourable conditions and can double their number in a matter of 20 minutes.
Question 14: Define Protozoa. Where are they found?
Answer: Protozoa are unicellular organisms with eukaryotic cell. They are found in soil, fresh water and sea water. Some are also found in the body of other organisms and are pathogenic in nature. These organisms reproduce by simple cell division.
Question 15: Give some examples of Protozoa.
Answer: Some examples of Protozoa include:
1. Amoeba, Paramoecium which freely live in dirty water.
2. Entamoeba histolytica –This causes amoebiasis.
3. Plasmodium vivax –This causes malaria
4. Euglena –autotrophic
Question 16: How do Fungi reproduce?
Answer: Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that reproduce sexually and asexually by cell division or by budding.
Question 17: Give some examples of Fungi.
Answer: Some examples of Fungi include Baker ’s yeast, Candida, Mushroom, etc.
Question 18: Define a virus.
Answer: In microbiology, viruses are organisms that live at the edge of living and non livings. Virus is a long molecule of DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid) or RNA (RiboNucleic Acid) which is surrounded by a protein coat.
Question 19: Where are Viruses found?
Answer: Viruses are extremely tiny, i.e. 10 to 100 times smaller than bacteria and can be viewed only under an electron microscope. They are found mostly as independent particles and multiple rapidly in living organisms.
Question 20: What is Algae? Give examples.
Answer: Algae are unicellular, eukaryotic, and autotrophic organisms which live in water. Some examples include Chlorella, Chlamydomonas, etc.
Question 21: Write the sizes of different microorganisms.
Answer: Given below are the sizes of different microorganisms:
1. Bacteria (size – 1 μm to 10 μm)
2. Protozoa (size –approximately 200 μm)
3. Fungi- (size- approximately 10 μm to 100 μm)
4. Algae- (size- approximately 10 μm to 100 μm)
5. Viruses-( size- approximately 10 nm to 100 nm)
Note:
1 meter = 106 micrometer (μm)
1 meter = 109 nanometer (nm)
Question 22: What is the criteria based on which Whittaker classified living organisms?
Answer: Whittaker’s classification of living organisms was done on the basis of the following criteria:
1. Complexity of cell structure: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
2. Complexity of organisms: Unicellular or Multicellular
3. Mode of nutrition: Plants –Autotrophic-Photosynthetic
Fungi- Saprophytic- Absorption from dead organisms
Animals- Heterotrophic and ingestive
4. Life style: Plants –Producers
Animals –Consumers
Fungi –Decomposers
5. Phylogenetic relationship: Prokaryotic to Eukaryotic, unicellular to multicellular
We hope that the above mentioned solutions of “MSBSHSE Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Living World and Classification of Microbes ” will help students build a strong foundation of the different concepts mentioned in the chapter.